In the world of equine care, the battle against parasitic intestinal worms stands as a an important component of maintaining horse health and vitality. These internal parasites, ranging from the notorious roundworms to the stealthy tapeworms, present significant health risks to horses of all ages. View our range of horse wormers and pastes.
Without diligent management, infestations can lead to malnutrition, weight loss, colic, and in severe scenarios, death. This article aims to delve into the complexities of these parasites, exploring their life cycles, the varied impacts they have on both young and adult horses, and the importance of a proactive approach in their management for a horse's health.
The main types of worms in horse are tape worms, round worms, bots worms, an pin worms.
The Silent Threat of Internal Parasites
Equine health is perpetually under siege by an array of parasitic worms, constituting a silent epidemic that affects horses globally. These parasites orchestrate a range of health complications, undermining the well-being and performance of these noble animals. The cornerstone of thwarting these potential crises lies in early detection coupled with effective management strategies.
Significance of Worm Control
Ensuring the health and productivity of equine companions necessitates a robust understanding of worm control. This discourse aims to unravel the types of worms that frequently infest horses, elucidating their detrimental effects and delineating strategic approaches for their prevention and treatment.
Understanding Worm Impact on Horse Health
Parasitic worms assault various bodily systems of their hosts, eliciting unique health challenges. The spectrum of impact is vast, ranging from debilitating nutritional deficiencies to critical organ damage, underscoring the imperative for comprehensive parasite control measures.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Organ Damage
Worms such as roundworms and tapeworms exploit the host's nutrients or inflict physical harm on organs. This parasitic burden can manifest in weight loss, deteriorating coat condition, and compromised organ functionality.
Immune System Compromise
The relentless onslaught of chronic worm infestations can weaken a horse's immune defenses, heightening susceptibility to other diseases and infections. This vulnerability accentuates the necessity for regular, efficacious worming interventions.
Key Parasites Affecting Horses
A pivotal step in effective parasite management is the identification of the most prevalent and perilous internal parasites. This segment delves into the life cycles, symptomatic presentations, and treatment modalities for the primary worms afflicting horses.
Roundworms: The Young Horse's Foe
Ascarids, predominantly targeting young horses, pose a significant threat through growth retardation and intestinal blockages. Their reproductive strategy involves the deposition of sticky yellow eggs, exacerbating existing worm burdens.
Diagnosis and Management
The employment of regular fecal egg counts and bespoke worming programs is vital in mitigating roundworm infestations, particularly among young foals and recently weaned foals.
Strongyles: Blood Vessel Invaders
Strongyles, encompassing both small and large variants, wreak havoc on horse health by damaging the gut wall and blood vessels, potentially leading to significant bleeding or fatal outcomes.
Targeted Control Measures
The formulation of strategic deworming plans, informed by fecal egg counts, alongside pasture management techniques such as rotational grazing, is crucial in curtailing strongyle populations.
Tapeworms: Colic Inducers
Positioned at the juncture of the small and large intestines, tapeworms frequently incite colic episodes. Their perilous nature and the health complications they induce categorize them among the most dangerous internal parasites.
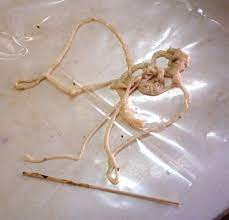
Effective Tapeworm Management
An annual regimen of praziquantel-containing products, tailored to the individual horse's risk profile, is advocated for tapeworm control.
Bots: Stomach Lining Irritants
The lifecycle of bot flies, from worm eggs deposition on the horse's coat to larval attachment to the stomach lining, results in significant irritation. The removal of bot fly eggs and the application of suitable dewormers are integral to management strategies for bot flies and bot eggs.
Pinworms: The Cause of Tail Rubbing
Pinworms, colonizing the large intestine, instigate intense anal itching as egg-laying adults, leading to tail rubbing and potential skin infections.
Hygiene and Treatment
A heightened focus on stable hygiene and targeted deworming protocols is paramount for the effective eradication of pinworm infestations.
Diagnostic Approaches to Worm Infestations
The early detection of worm infestations via diagnostic methodologies like fecal egg counts is a cornerstone of effective management. This section outlines the arsenal of tools and techniques at our disposal for diagnosing worm burdens in horses.
Faecal Egg Counts: Monitoring Worm Burdens
Regular fecal egg counts are instrumental in identifying the types and severities of worm infestations, guiding the development of targeted worming programs.
Blood Tests and Ultrasounds
For severe infestations, blood tests and ultrasounds offer invaluable insights into the impact on internal organs, informing subsequent treatment strategies.
Advanced Worming Strategies
Crafting an efficacious worming strategy is imperative for controlling worm burdens in horses. This entails a comprehensive understanding of parasite life cycles, identifying horses at high risk, and implementing targeted treatments.
Targeted Worming Programmes
The creation of a targeted worming program, calibrated to the horse's age, health status, and exposure risk, is essential for the effective containment of parasite populations.
Pasture Management and Rotational Grazing
The adoption of pasture management practices, including rotational grazing and the regular removal of manure, plays a significant role in diminishing environmental worm burdens.
Nutrition's Role in Parasite Management
Optimal nutrition is a keystone in bolstering a horse's immune system and overall health, thereby aiding in the management of worm burdens.
High-Fiber Diets and Supplements
A diet rich in fiber, supplemented with probiotics, can enhance gut health and fortify resistance against parasitic invasions.
Emerging Trends in Equine Parasite Management
Keeping abreast of the latest research and advancements in equine parasite management is vital for ensuring the continued health and well-being of horses.
Innovations in Worm Control
The exploration of vaccines, genetic predispositions to infestations, and novel deworming compounds presents promising pathways for the augmentation of parasite control measures.
Conclusion: Towards Comprehensive Worm Management
The orchestration of effective worm management in horses demands an integrated approach, encompassing regular diagnostics, strategic deworming, nutritional optimization, and a commitment to staying informed about the latest developments in parasite control. By embracing these comprehensive strategies, horse owners can safeguard their charges from the myriad threats posed by internal parasites, thereby ensuring their health, performance, and longevity.




